02. Differentiation Recap
Differentiation Recap
In the last lesson, you learned about the derivative. This section is just here to remind you of what you learned.
Understanding the Derivative
You saw a few ways to understand the derivative:
1. The "Rate of Change" Interpretation
If f(t) gives the value of a function at any t, then \dot{f}(t_0) gives the instantaneous rate of change of f(t) at the value t=t_0.
2. The Graphical Interpretation
The slope of the line tangent to f(t) at t=t_0 is \dot{f}(t_0)
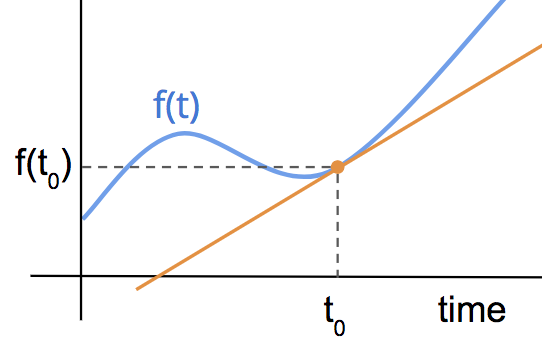
The slope of the orange line is equal to the derivative of f at t=t_0
3. The Formal Definition
The formal mathematical definition is the following:
The derivative of a function f(t) is the function \dot{f}(t) (or \frac{df}{dt}), and is defined as:
Derivatives and Motion
Position, velocity, and acceleration are all useful quantities when describing a vehicle's motion and these quantities are related through the derivative.
velocity is the derivative of position
- v(t)=\dot{x}(t)
acceleration is the derivative of velocity and the second derivative of position.
- a(t) = \dot{v}(t) = \ddot{x}(t)
Coding the Derivative
def get_derivative_from_data(position_data, time_data):
"""
Calculates a list of speeds from position_data and
time_data.
Arguments:
position_data - a list of values corresponding to
vehicle position
time_data - a list of values (equal in length to
position_data) which give timestamps for each
position measurement
Returns:
speeds - a list of values (which is shorter
by ONE than the input lists) of speeds.
"""
# 1. Check to make sure the input lists have same length
if len(position_data) != len(time_data):
raise(ValueError, "Data sets must have same length")
# 2. Prepare empty list of speeds
speeds = []
# 3. Get first values for position and time
previous_position = position_data[0]
previous_time = time_data[0]
# 4. Begin loop through all data EXCEPT first entry
for i in range(1, len(position_data)):
# 5. get position and time data for this timestamp
position = position_data[i]
time = time_data[i]
# 6. Calculate delta_x and delta_t
delta_x = position - previous_position
delta_t = time - previous_time
# 7. Speed is slope. Calculate it and append to list
speed = delta_x / delta_t
speeds.append(speed)
# 8. Update values for next iteration of the loop.
previous_position = position
previous_time = time
return speeds